The Indian rupee has plunged to a historic low of 85.81 against the US dollar, reflecting a period of significant weakness in the currency market. This decline is influenced by a combination of global and domestic factors, ranging from geopolitical tensions to the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions. Let’s delve into the key aspects contributing to this depreciation and its broader implications.
Geopolitical and Economic Backdrop
The Federal Reserve’s recent 0.25% rate cut has created ripples across global markets. Although the Fed is expected to maintain rates at their current levels in January, its stance has bolstered the US dollar index, which measures the dollar’s performance against a basket of six major currencies. The Dollar index climbed to 108.44 on December 19, indicating a stronger dollar that has added pressure on emerging market currencies, including the rupee. Additionally, the yield on the US 10-year Treasury bond rose to 4.56% on the same day, further tightening financial conditions for global markets.
India’s Forex Reserves and Trade Dynamics
India’s foreign exchange reserves have declined to USD 654.86 billion as of December 6, a sharp fall from the peak of USD 704.885 billion recorded on October 4. This reduction highlights the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) interventions in the forex market to stabilize the rupee. Despite this, India’s services trade surplus rose to USD 18 billion in November, compared to USD 17.1 billion in October, offering some cushion to the overall balance of payments.
The weakening yuan has also compounded challenges for Asian currencies, including the rupee. A depreciating Chinese currency increases the competitiveness of Chinese exports, putting pressure on other regional currencies to follow suit.
Domestic Economic Challenges
India’s domestic economic landscape has added to the rupee’s struggles. High inflation continues to erode purchasing power, with core inflation remaining sticky despite policy efforts. Sluggish industrial growth and subdued rural demand have further constrained economic momentum. Additionally, the widening fiscal deficit has raised concerns among investors, creating downward pressure on the currency.
The government’s reliance on borrowing to fund expenditures has increased bond yields domestically, making it costlier to raise capital. This, coupled with a tepid recovery in private investment, has limited India’s ability to counter external economic shocks effectively.
The Trump Era’s Lingering Impact
Although Donald Trump’s presidency has ended, its effects on global trade policies and economic relations are still felt. Protectionist measures and trade tensions initiated during his tenure have left enduring challenges for emerging economies like India. These factors have indirectly influenced the rupee’s performance by creating a less favorable trade environment.
Technical summary
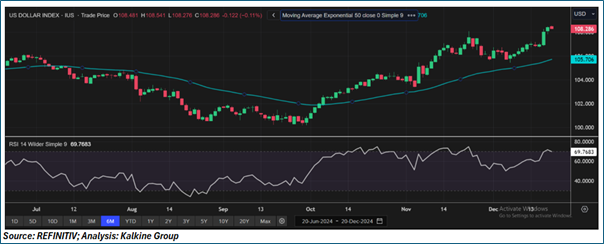
The US Dollar Index (DXY) is currently in a strong uptrend, with prices consistently trading above the 50-day exponential moving average (EMA), which acts as dynamic support. Momentum remains robust, as evidenced by the formation of higher highs and higher lows since the recovery began in September. The RSI stands at 69.76, nearing the overbought territory, signaling potential short-term exhaustion of the bullish momentum. Key support levels to watch are at 105.70, aligned with the 50-day EMA, and 104.00, based on horizontal price consolidations in October. On the upside, the index is testing a critical resistance zone at 108.50-108.60, with a breakout potentially leading to a move toward the psychological level of 110.00. However, a pullback remains possible if overbought conditions persist, making the 50-day EMA a crucial level to monitor for sustained bullish momentum.
Looking Ahead
With the Federal Reserve expected to keep interest rates unchanged in its January meeting and geopolitical tensions continuing, the Indian Rupee is likely to face sustained pressure. The Reserve Bank of India's efforts to manage currency volatility, alongside structural reforms aimed at boosting exports and attracting foreign investment, will be crucial in navigating this challenging period.
While India’s economy shows resilience in areas such as services trade, broader global dynamics, including the strength of the US dollar and rising bond yields, will likely continue to exert downward pressure on the rupee. Market participants will closely monitor developments in global monetary policies, trade balances, and geopolitical events to assess the rupee's trajectory in the coming months.
The rupee's persistent weakness also raises concerns about imported inflation, particularly in critical sectors such as energy and electronics. Additionally, the depreciation could impact corporate earnings, especially for businesses that rely heavily on dollar-denominated imports.
