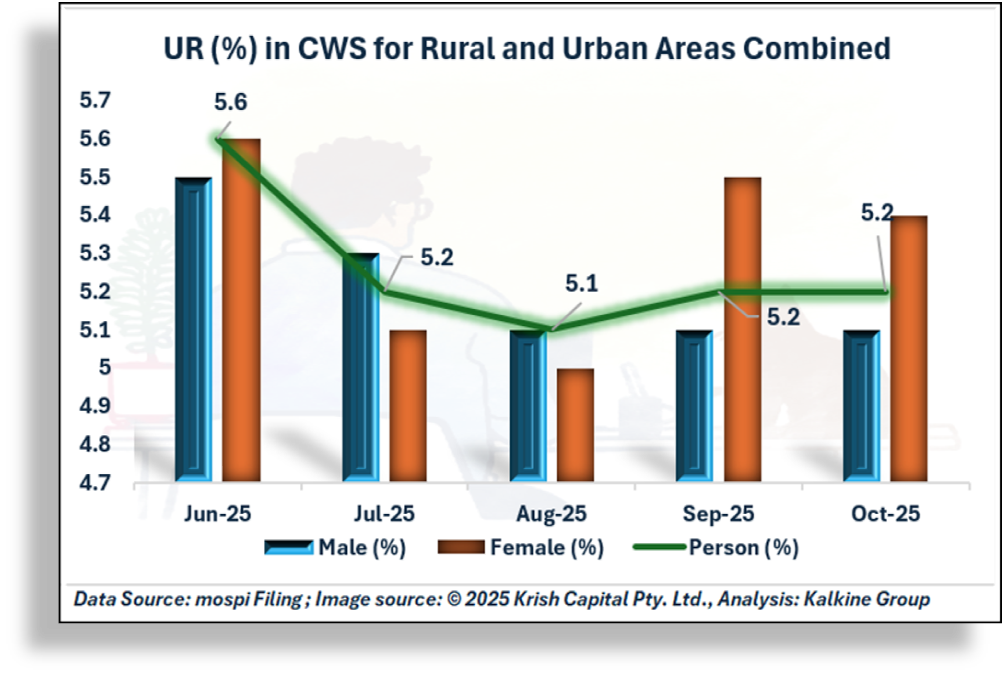
India’s labour market remained broadly stable in October 2025, with the overall unemployment rate holding steady at 5.2%. Urban areas saw a modest increase in job participation, highlighting the nuanced recovery in employment amid evolving economic conditions.
Urban Employment Shows Moderate Improvement
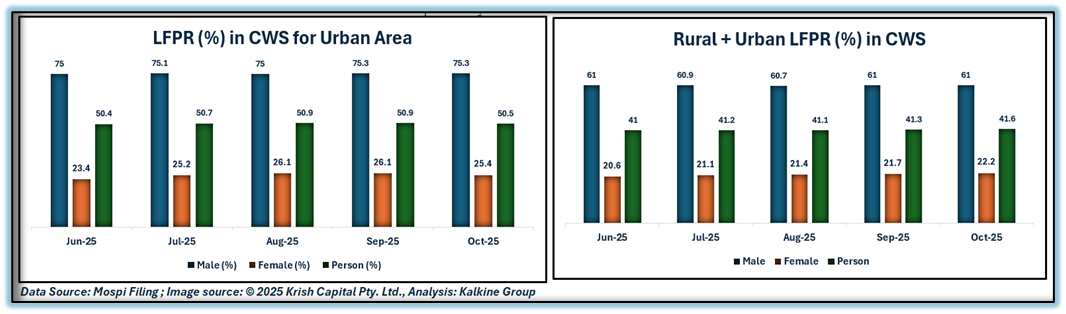
The urban workforce witnessed a slight uptick in participation, particularly among men, reflecting gains in services, manufacturing, and emerging sectors. Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR) in urban areas for persons aged 15 years and above stood at 50.5%, with male participation at 75.3% and female participation at 25.4%.
For the younger demographic (ages 15–29 years), LFPR was 41.6%, with male youth at 61% and female youth at 22.2%, indicating steady engagement of young workers in the urban economy.
Rural Workforce Remains Strong
Rural labour participation remained robust, supported by agriculture and allied activities. LFPR for rural areas among persons aged 15+ was 57.8% in October 2025, with male participation at 78.4% and female at 38.4%. Among rural youth aged 15–29 years, participation reached 41.7%, with 61.8% of young men and 22.4% of young women engaged in economic activity.
Month-on-month data from June to October 2025 shows a gradual upward trend in rural participation, underscoring the resilience of the rural labour market amid ongoing economic transitions.
Combined Rural and Urban Trends
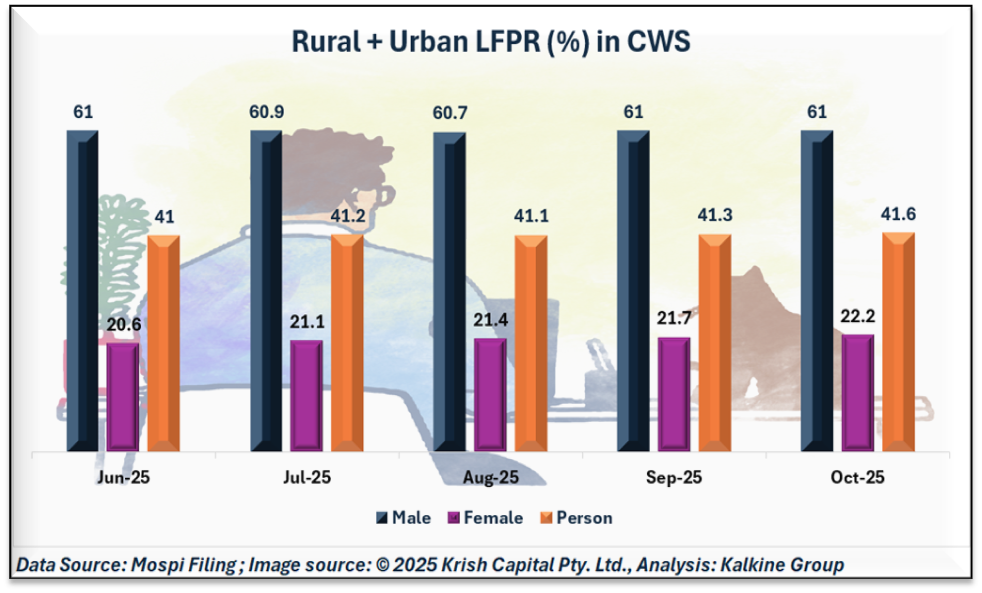
Overall, combining rural and urban sectors, the LFPR among persons aged 15+ reached 55.4% in October 2025. Youth participation (15–29 years) across India stood at 41.6%, reflecting balanced engagement across genders and regions.
The consistent participation rates highlight the importance of inclusive policies that encourage employment among women and young adults, particularly in urban areas where female labour force participation remains comparatively low.
Policy Implications: Strengthening Employment Opportunities
Labour economists emphasize the need for targeted initiatives to boost female participation and youth employment. Strategies such as skill development programs, incentives for formal sector employment, and investment in urban infrastructure projects can help sustain job growth and reduce regional disparities.
Conclusion
India’s unemployment rate remaining steady at 5.2% in October 2025 signals stability in the labour market, even as urban job opportunities witness moderate gains. Ensuring sustainable and inclusive growth will require a focus on expanding employment opportunities for youth and women, alongside strengthening rural livelihoods to maintain balanced national workforce participation.
