India has established itself as the global frontrunner in real- time digital payments, driven by the expansive relinquishment of the Unified Payments Interface (UPI). As highlighted in a recent IMF report titled "Growing Retail Digital Payments: The Value of Interoperability," UPI now processes more than 18 billion transactions each month a milestone that reflects India's rapid shift toward a digitally driven economy.
Digital Payments Revolution
Launched in 2016 by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) has revolutionized the way financial transactions are carried out across the country. By enabling instant money transfers through a mobile interface that links multiple bank accounts, UPI has made peer-to-peer payments, merchant transactions, and bill settlements seamless and efficient.
In June 2025 alone, UPI processed over ₹24.03 lakh crore through 18.39 billion transactions, marking a remarkable 32% year-on-year growth. Today, UPI powers approximately 85% of India’s digital payments and handles close to 50% of all real-time payments worldwide.
Its widespread use reflects the platform’s scalability and versatility in catering to both consumers and businesses. With connectivity across 675 banks, UPI currently serves 491 million users and 65 million merchants creating one of the most inclusive and integrated digital payment ecosystems globally.
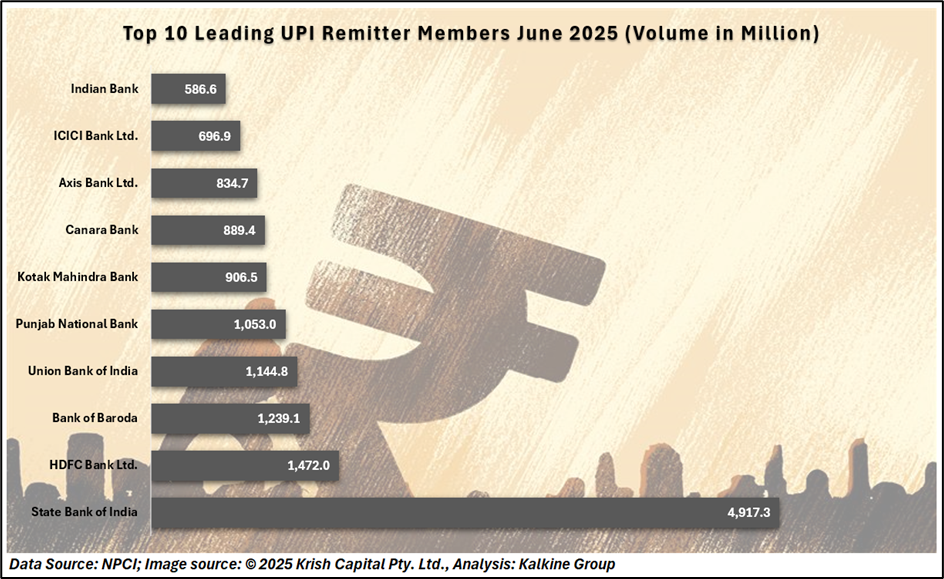
Enhancing Economic Access
The widespread success of UPI is rooted in India’s larger agenda of advancing financial inclusion. A key milestone in this journey was the launch of the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) in 2014, which enabled over 550 million previously unbanked individuals to access the formal banking system. This foundational infrastructure set the stage for UPI to emerge as a secure, affordable, and easy-to-use digital payment solution.
UPI’s speed, transparency, and interoperability have significantly reduced transaction costs while improving financial accountability. For small enterprises, it has minimized dependence on cash and enabled instant settlements, fostering better liquidity. For consumers—especially in rural and underserved regions—UPI has made digital transactions more inclusive and accessible.
Moreover, the government’s increasing reliance on digital platforms for distributing subsidies, welfare payments, and pensions has further strengthened financial transparency. UPI’s role in powering these direct benefit transfers has been crucial in bringing millions into the formal economic fold, accelerating India’s journey toward a digitally empowered society.
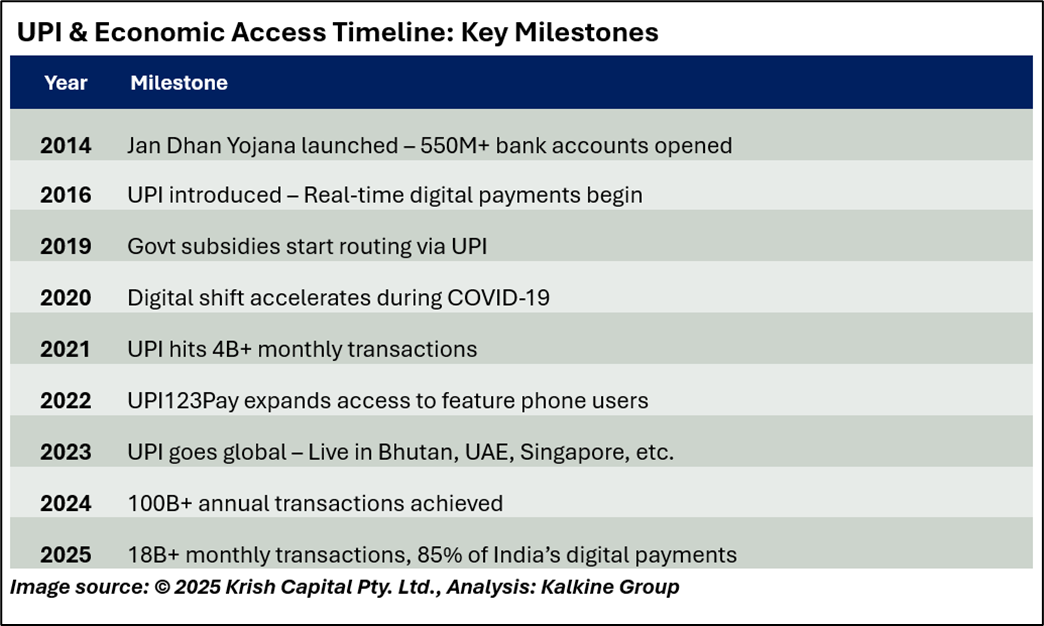
Expanding UPI’s Global Footprint
UPI is expanding beyond India, now live in seven countries including the UAE, Singapore, France, and Mauritius, allowing Indian trippers and NRIs to use a familiar payment system abroad. Its launch in France marks a strategic step into the European request.
India is also championing for UPI relinquishment among BRICS nations to streamline cross-border remittances and trade, potentially lowering costs and perfecting effectiveness especially significant given India’s$ 100 billion in periodic remittance inrushes.
Encyclopaedically, UPI’s rise boosts India’s digital tactfulness and positions it as a leader in scalable, low- cost fiscal structure.
Conclusion
UPI’s rapid growth has positioned India at the forefront of the global digital payment’s revolution. By enhancing financial inclusion, reducing transaction costs, and expanding internationally, UPI is not just transforming how money moves it is redefining India’s role in shaping the future of digital finance.
